THE VASER® SYSTEM
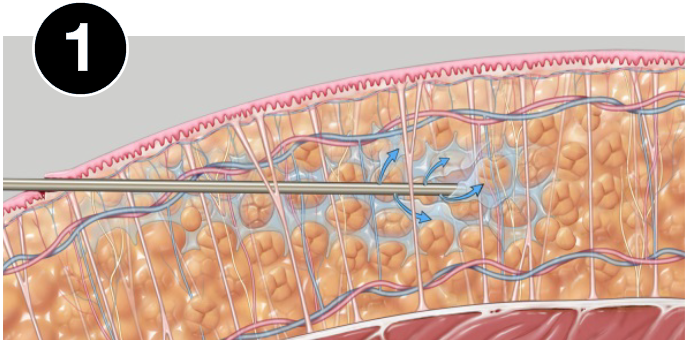
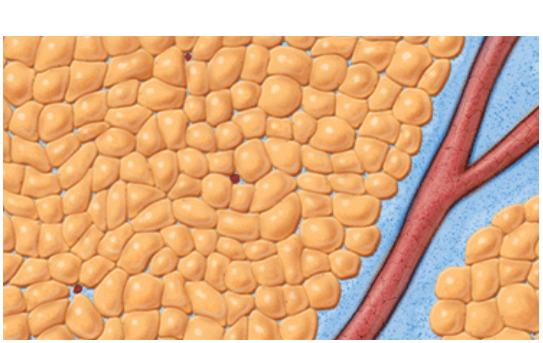
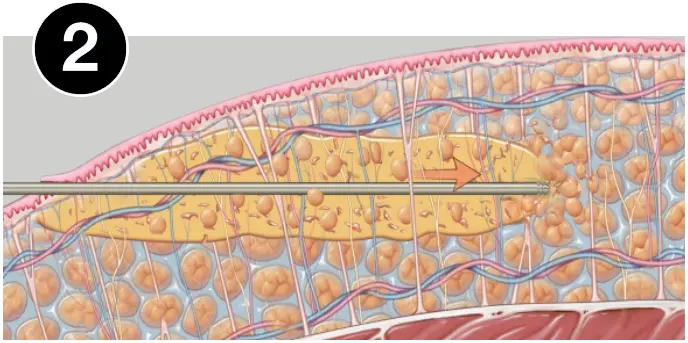
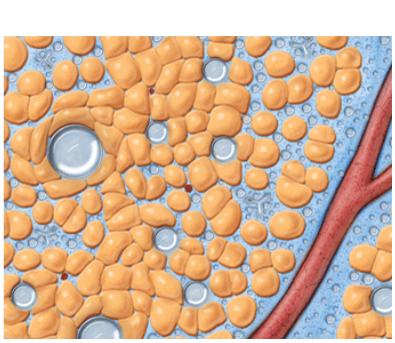
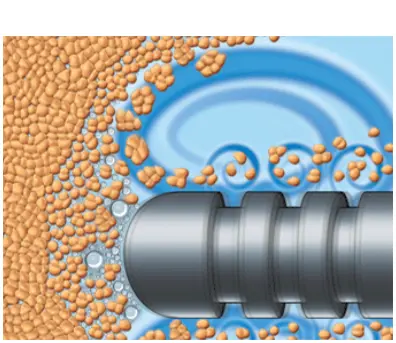
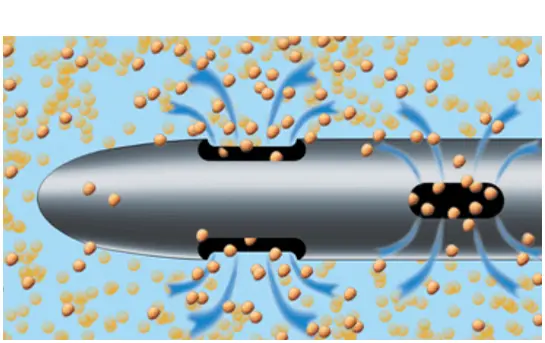
VASER® is precise ultrasound-assisted technology combining mechanical and acoustic fragmentation/emulsification
of fat, designed to optimize procedure speed and efficiency while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissue.1-3
Replaceable Suction Filter
Easy access to filter location for trapping any overflowing fat/fluids
VASER® Ultrasonic Amplifier
Efficient fragmentation of fatty tissue using continuous and/or pulsed wave energy with convenience display to track activation time
VentX® Infiltration & Aspiration Console
Quiet, efficient removal of fatty tissue with precise suction pressure control to preserve fat cell viability3-6
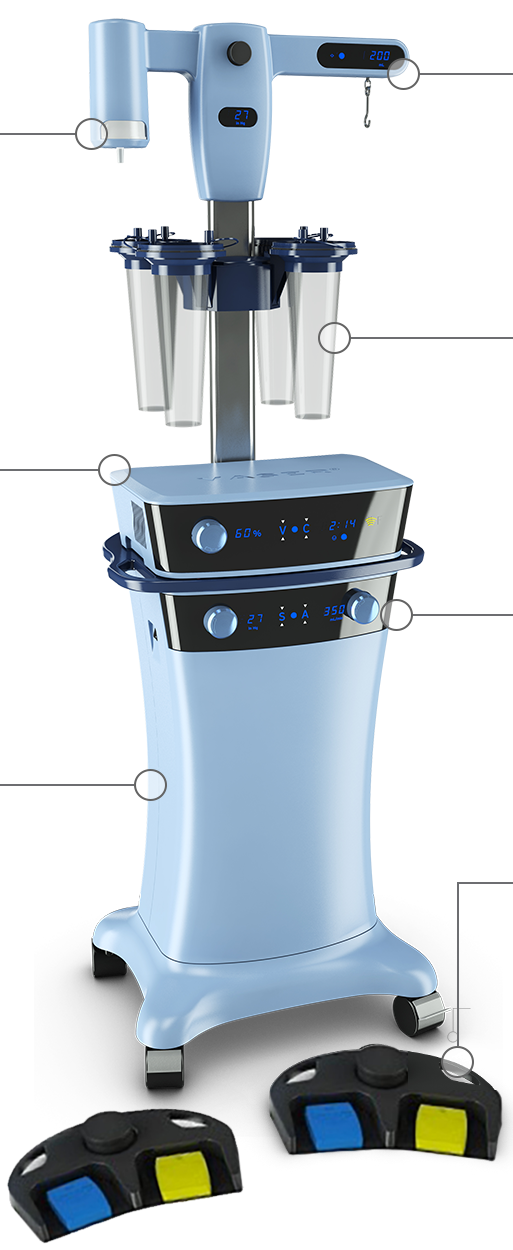

Precision Fluid Management™ System
Simplified and precise tracking of fluid by measuring infiltrate volume up to 4500mL
Universal Canister/Utility Rack
Adaptable sliding slots allow attachment of up to four 1,250cc collection canisters or other utilities and accessories
Peristaltic Infiltration Pump (not visible)
Smooth infiltration that is adjustable
and reversible
Wireless Footswitch (optional)
Untethered positioning for convenient and easy control over infiltration and ultrasound activation
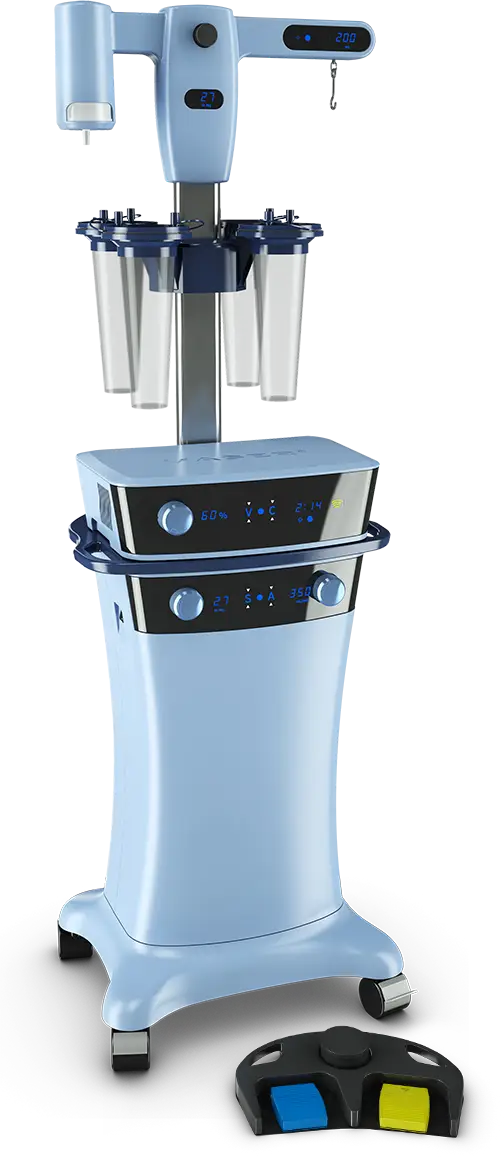

Replaceable Suction Filter
Easy access to filter location for trapping any overflowing fat/fluids
VASER® Ultrasonic Amplifier
Efficient fragmentation of fatty tissue using continuous and/or pulsed wave energy with convenient display to track activation time2,3
VentX® Infiltration & Aspiration Console
Quiet, efficient removal of fatty tissue with precise suction pressure control to preserve fat cell viability3-6
Precision Fluid Management™ System
Simplified and precise tracking of fluid by measuring infiltrate volume up to 4500mL
Universal Canister/Utility Rack
Adaptable sliding slots allow attachment of up to four 1,250cc collection canisters or other utilities and accessories
Peristaltic Infiltration Pump (not visible)
Smooth infiltration that is adjustable and reversible
Wireless Footswitch (optional)
Untethered positioning for convenient and easy control over infiltration and ultrasound activation
1. Cimino WW. Ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty: basic physics, tissue interactions, and related results/complications. In: Prendergast PM, Shiffman MA, eds. Aesthetic medicine: Art and techniques. Berlin: Springer; 2011:519-528
2. Jewell M. Innovation in Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery Lipoplasty. In: Eisenmann-Lkein M, Neuhann-Lorenz C, eds. Lipoplasty Innovations in Plastic and Aesthetic Surgery. Berlin: Springer; 2008:443-453.
3. VASER®/VentX operator manual
4. Schafer ME. Ultrasonic surgical devices and procedures. In: Gallego-Juárez JA, Graff KF, eds. Power Ultrasonics: Applications of High-Intensity Ultrasound. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing; 2015:633-660.
5. Schafer ME, Hicok KC, Mills DC, Cohen SR, Chao JJ. Acute adipocyte viability after third-generation ultrasound-assisted liposuction. Aesthet Surg J. 2013 Jul;33(5):698-704.
6. Fisher C, Grahovac TL, Schafer ME, Shippert RD, Marra KG, Rubin JP. Comparison of harvest and processing techniques for fat grafting and adipose stem cell isolation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 013;132(2):351-61.
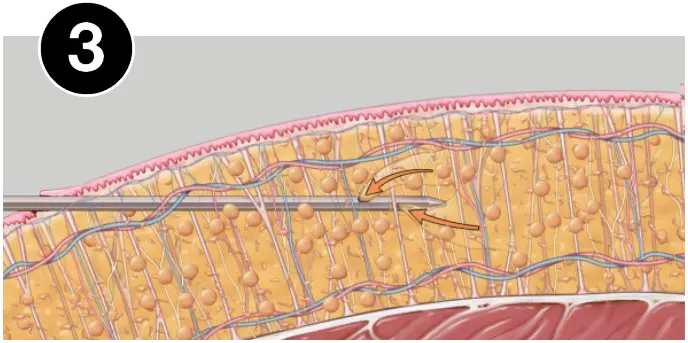
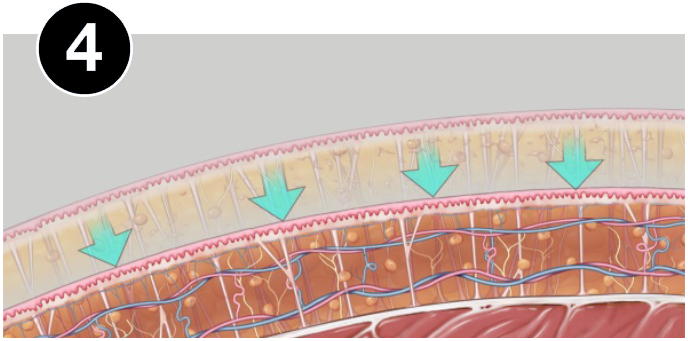
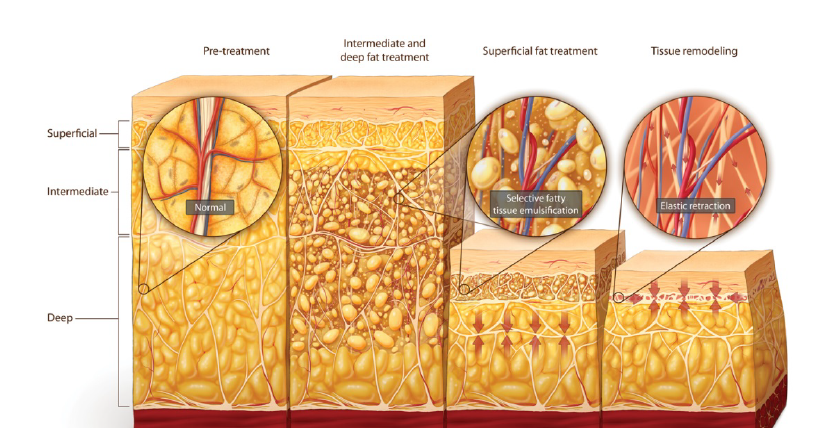
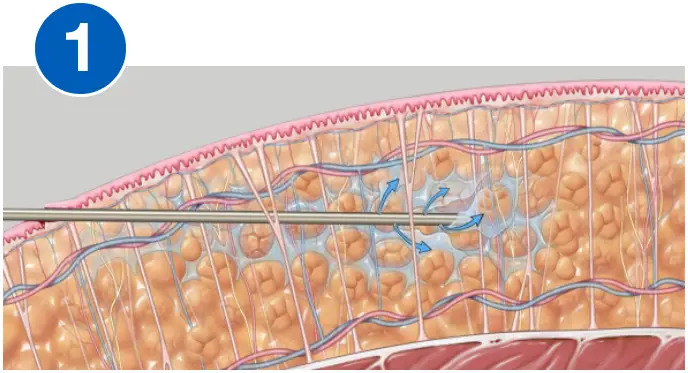
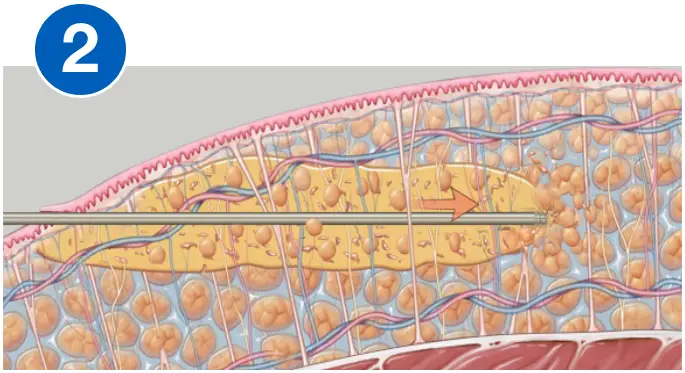
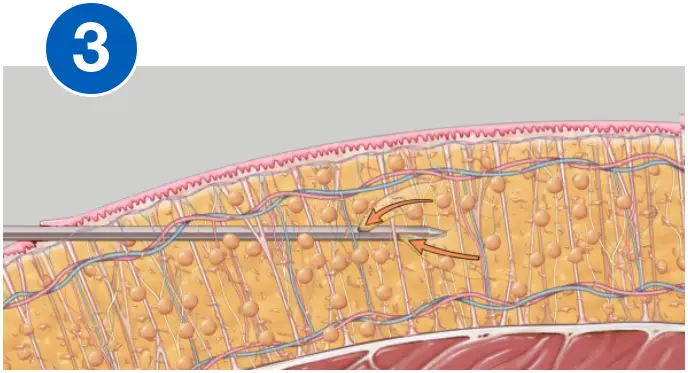
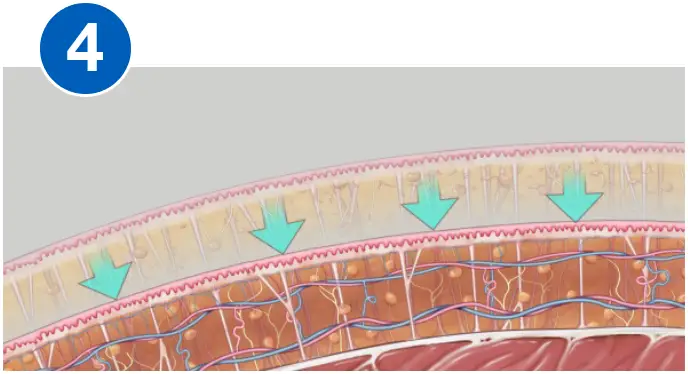
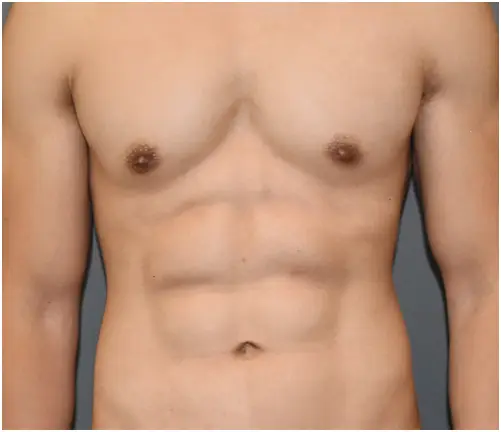
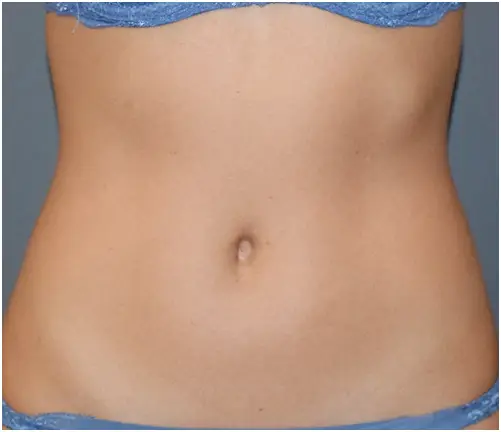
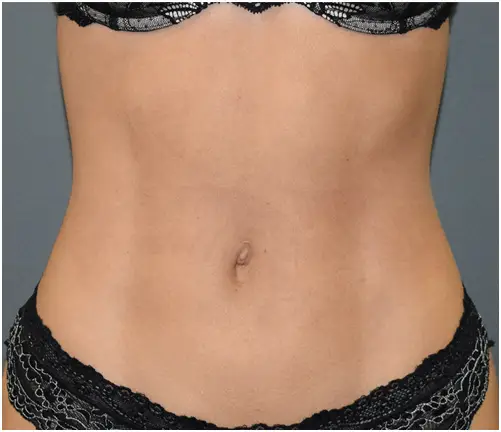
HOW VASER WORKS
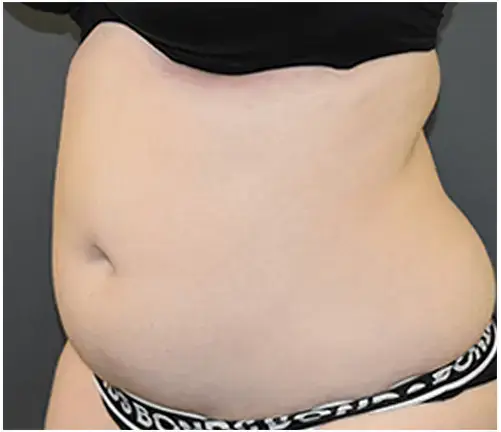
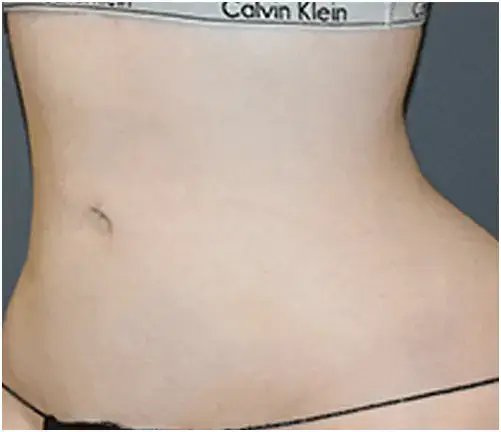
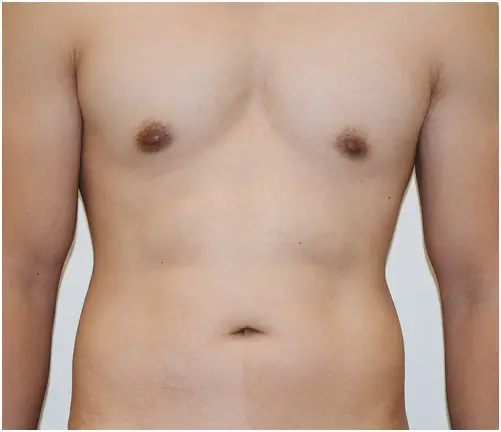
THE  DIFFERENCE
DIFFERENCE
1. Garcia O Jr. Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction: Current Concepts and Techniques. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland; 2020.
1. Garcia O Jr. Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction: Current Concepts and Techniques. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland; 2020. 2. Cimino WW. Ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty: basic physcis, tissue interactions, and related results/complications. In: Prendergast PM, Shiffman MA, eds. Aesthetic Medicine: Art and Techniques. Berlin: Springer; 2011:519-528. 3. Hoyos AE, Prendergast PM. VASER technology for ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty. In: High Definition Body Sculpting: Art and Advanced Lipoplasty Techniques. Berlin: Springer; 2014:73-81. 4. Schafer ME. Ultrasonic surgical devices and procedures. In: Gallego-Juarez JA, Graff KF, eds. Power Ultrasonics: Applications of High-Intensity Ultrasound. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing; 2015:633-660. 5. Schafer ME, et al. Acute adipocyte viability after third-generation ultrasound-assisted liposuction. Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33(5):698-704. 6. Schafer ME. Basic science of ultrasound in body contouring. In: Garcia O Jr, ed. Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction: Current Concepts and Techniques. Berlin: Springer; 2020:9-21.
1. Garcia O Jr. Ultrasound-assisted liposuction: Current concepts and techniques. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland; 2020. 2. Duscher D, Atashroo D, Maan ZN, et al. Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction Does Not Compromise the Regenerative Potential of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(2):248‐257.
1. Garcia O Jr. Ultrasound-Assisted Liposuction: Current Concepts and Techniques. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland; 2020. 2. Di Giuseppe A. Vaser abdominal contouring. In: Di Giuseppe A, Shiffman MA, eds. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery of the Abdomen. Switzerland: Springer; 2016:309-340. 3. Adapted from: Garcia O. Ultrasonic Liposuction. In: Rubin JP, Jewell ML, Richter DF, et al, editors. Body Contouring and Liposuction. Elsevier Saunders Publishers, NY, NY. 2013; p543-558.